It is a common misconception that lithium iron phosphate batteries are different than lithium-ion batteries. In reality, there are many types of lithium-ion batteries, and lithium iron phosphate is just one of them.
Let’s take a look at what exactly lithium iron phosphate is, why it’s a great choice for certain types of batteries, and how it compares to other lithium-ion battery options.
What is Lithium Iron Phosphate?
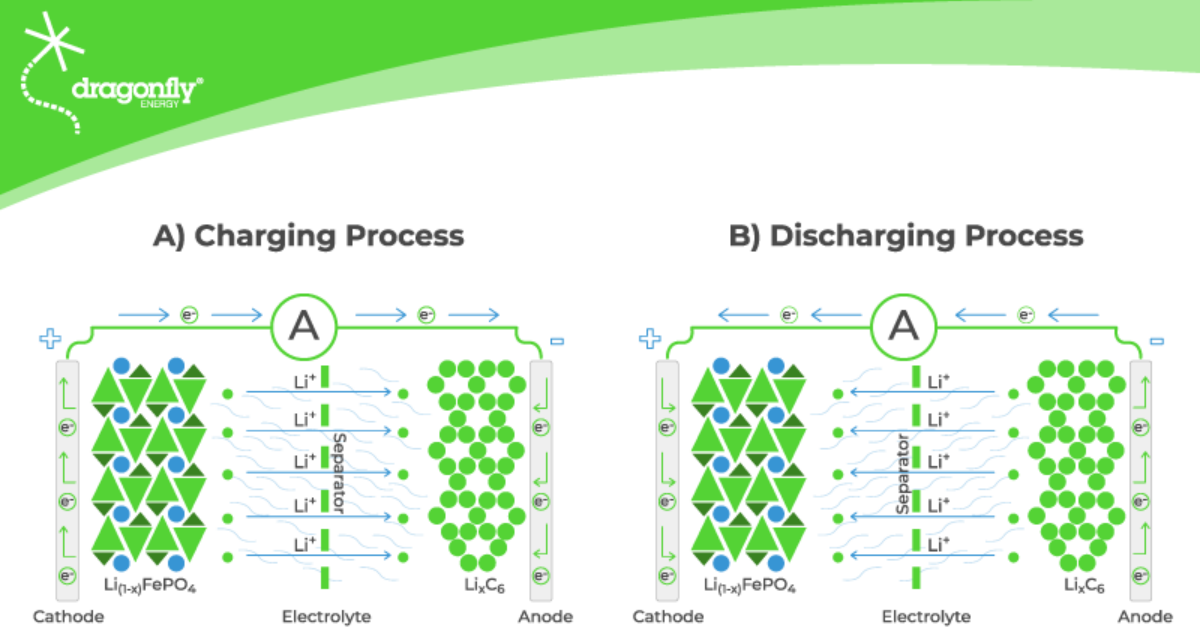
Lithium iron phosphate is a chemical compound LiFePO4 or “LFP” for short. LFP offers good electrochemical performance, low resistance and is one of the safest and most stable cathode materials available for lithium-ion batteries.
What is a Lithium Iron Phosphate Battery?
Lithium iron phosphate batteries are a type of lithium-ion battery that uses lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material to store lithium ions. LFP batteries typically use graphite as the anode material. The chemical makeup of LFP batteries gives them a high current rating, good thermal stability, and a long lifecycle.
Most lithium iron phosphate batteries have four battery cells wired in series. The nominal voltage of an LFP battery cell is 3.2 volts. Connecting four LFP battery cells in series results in a 12-volt battery that is an excellent replacement option for many 12-volt lead-acid batteries.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Vs. Alternative Lithium-Ion Types
Lithium iron phosphate is just one of the many types of lithium-ion batteries. Changing the chemical compound for the cathode creates different kinds of lithium-ion batteries. Some of the most common options are Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LCO), Lithium Manganese Oxide (LMO), Lithium Nickel Cobalt Aluminum Oxide (NCA), Lithium Nickel Manganese Cobalt Oxide (NMC), and Lithium Titanate (LTO).
Each of these battery types has varying strengths and weaknesses that make them a good fit for different applications. Looking at the main properties of these battery types, we can see where lithium iron phosphate batteries stand and for which applications they are best.
Energy Density
LFP batteries have one of the highest specific power ratings amongst other lithium-ion types. In other words, high specific power means that LFP batteries can deliver high amounts of current and power without overheating.
On the other hand, it is important to keep in mind that LFP batteries have one of the lowest specific energy ratings. Low specific energy means that LFP batteries have less energy storage capacity per weight than other lithium-ion options. This is typically not a big deal because increasing the battery bank’s capacity can be done by connecting multiple batteries in parallel. This may not be ideal for an application where extreme energy density in a very light space is required, like battery electric vehicles.
Battery Life Cycles
Lithium iron phosphate batteries have a life span that starts at about 2,000 full discharge cycles and increases depending on the depth of discharge. Cells and the internal battery management system (BMS) used at Dragonfly Energy have been tested to over 5,000 full discharge cycles while retaining 80% of the original battery’s capacity.
LFP is second only to lithium titanate in lifespan. However, LTO batteries have traditionally been the most expensive lithium-ion battery option, making them cost-prohibitive for most applications.
Discharge Rate
Discharge rate is measured in a multiple of the battery’s capacity, meaning a 1C discharge rate for a 100Ah battery is 100A continuous. Commercially available LFP batteries traditionally have a 1C continuous discharge rating but can exceed this for short periods depending on the battery management system.
LFP cells themselves typically can provide a 25C discharge for short periods safely. The ability to exceed 1C allows you to use LFP batteries in high-power applications that may have startup spikes in the current draw.
Operating Temperatures
LFP batteries don’t enter thermal runaway conditions until around 270 degrees Celsius. Compared to the other common lithium-ion battery options, LFP batteries have the second-highest operating temperature limit.
Exceeding the temperature limit on a lithium-ion battery causes damage and can lead to thermal runaway, possibly resulting in a fire. The high operating limit of LFP significantly decreases the chance of a thermal runaway event. Combined with a high-quality BMS to shut down the cells well before these conditions (at around 57 degrees Celsius), LFP offers significant safety advantages.
Safety Advantages
LFP batteries are one of the stable chemistries of all of the lithium-ion options. This stability makes them one of the safest options for both consumer-facing and industrial applications.
The only other comparably safe option is lithium titanate, which again is typically cost-prohibitive and does not operate at the correct voltage in most situations for a 12V replacement.
Lithium Iron Phosphate Vs. Lead-Acid Batteries
Lithium iron phosphate batteries offer many advantages over traditional lead-acid batteries. The most notable is that LFP batteries have about four times the energy density of lead-acid batteries. You can deep-cycle LFP batteries repeatedly without damaging them. They also recharge 5 faster than lead-acid batteries.
This high energy density leads to a longer run time while simultaneously reducing the weight of the battery system.
The chemical reaction inside lead-acid batteries causes off-gassing, which requires the batteries to be vented and periodically refilled with water by the user. If the batteries are not stored upright, the acid solution can leak, damaging the battery and causing a mess. Alternatively, LFP batteries do not off-gas and do not need to be vented or refilled. Even better, you can mount them in any orientation.
LFP batteries are initially more expensive than lead-acid batteries. However, the long life span of LFP batteries balances out their high upfront cost. In most cases, LFP batteries will last 5-10 times longer than lead-acid batteries, resulting in significant overall cost savings.
Best Lithium Iron Phosphate Batteries For Replacing Lead-Acid Battery Applications
Many different lithium-ion batteries are available, and some even exceed lithium iron phosphate in certain performance categories. However, when it comes to replacing 12-volt lead-acid batteries, LFP is the best option available.
The main reason for this is that the nominal cell voltage for lithium iron phosphate is 3.2 volts. The nominal voltage of a 12-volt lead-acid battery is about 12.7 volts. Thus, wiring four cells in series inside of a battery yields 12.8 volts (4 x 3.2 = 12.8) – almost a perfect match! This is not possible with any other lithium-ion battery type.
Beyond a nearly perfect voltage match, LFP offers other advantages as a lead-acid replacement. As discussed above, LFP batteries are long-lasting, stable, safe, durable, lightweight, and have a high energy density. This makes them an excellent fit for many applications! Things like trolling motors, RVs, golf carts, and more applications that have traditionally relied on lead-acid batteries.
Dragonfly Energy and Battle Born Batteries build some of the best lithium iron phosphate batteries available. They are proudly designed and assembled in the United States with the highest quality materials available. In addition, each battery is rigorously tested and UL listed.
Each battery also includes an integrated battery management system to ensure the battery operates safely under all conditions. Dragonfly Energy and Battle Born Batteries have thousands of batteries installed and operating safely in many different applications worldwide.
Now You Know
In conclusion, lithium iron phosphate is just one of the many different types of lithium-ion batteries available. However, the unique set of characteristics that make up LFP batteries make them a fantastic alternative to 12-volt lead-acid batteries of the past.
Post time: Sep-30-2022